

Clindamycin is also sometimes used to treat bacterial vaginosis (an infection caused from too much of certain bacteria in the vagina). Clindamycin is also sometimes used to treat ear infections, tonsillitis (infection that causes swelling of the tonsils), pharyngitis (infection that causes swelling in the back of the throat), and toxoplasmosis (an infection that may cause serious problems in people who do not have healthy immune systems or in unborn babies whose mothers are infected) when these conditions cannot be treated with other medications. If you stop taking clindamycin too soon or skip doses, your infection may not be completely treated and the bacteria may become resistant to antibiotics.Ĭlindamycin is also sometimes used to treat acne and is used along with other medications to treat anthrax (a serious infection that may be deliberately spread as part of a terror attack) and malaria (a serious infection that is spread by mosquitoes in certain parts of the world). Take clindamycin until you finish the prescription, even if you feel better. If your symptoms do not improve or if they get worse, call your doctor. You should begin to feel better during the first few days of treatment with clindamycin.
CLINDAMYCIN SKIN RASH FULL
Take the capsules with a full glass of water so that the medication will not irritate your throat. Shake the liquid well before each use to mix the medication evenly. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
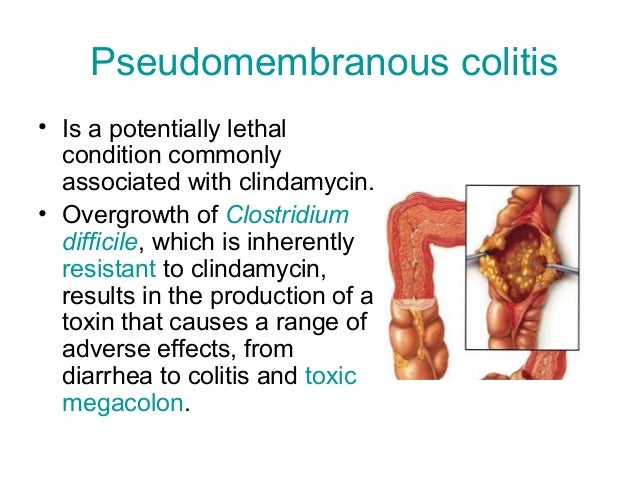
Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take clindamycin at around the same times every day. The length of your treatment depends on the type of infection you have and how well you respond to the medication. It is usually taken three to four times a day. Am Fam Physician. 2015 Feb 1 91(3):185-190.Clindamycin comes as a capsule and a solution (liquid) to take by mouth. Diagnosis and treatment of seborrheic dermatitis. Management of tinea corporis, tinea cruris, and tinea pedis: A comprehensive review. doi:10.2147/CCID.S137870Ĭenters for Disease Control and Prevention. Therapeutic management of classic lichen planopilaris: a systematic review. Lichen planopilaris.Įrrichetti E, Figini M, Croatto M, Stinco G. National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences: Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center. doi:10.1111/j.Ĭenters for Disease Control and Prevention. Efficacious and safe management of moderate to severe scalp seborrhoeic dermatitis using clobetasol propionate shampoo 0.05% combined with ketoconazole shampoo 2%: a randomized, controlled study. Dandruff, cradle cap, and other scalp conditions.

Candida infections, causes, targets, and resistance mechanisms: traditional and alternative antifungal agents. Malassezia-Associated Skin Diseases, the Use of Diagnostics and Treatment. National Organization for Rare Disorders. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Interventions for bacterial folliculitis and boils (furuncles and carbuncles). First step in the differential diagnosis of folliculitis: cytology.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
